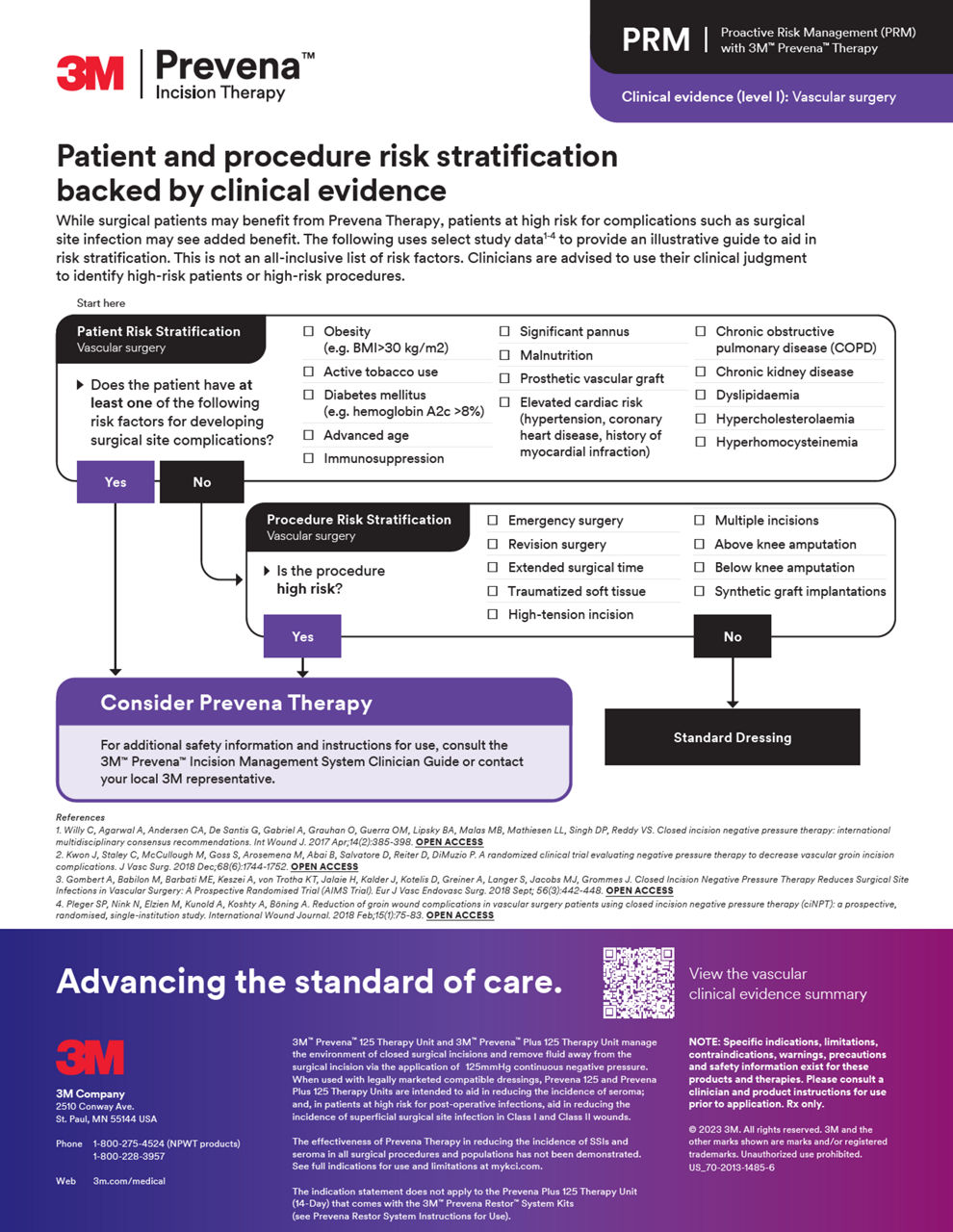
3M Prevena 治療用於血管手術
使用Prevena治療提升血管手術成果
針對血管手術程序的6項研究進行的系統性回顧和統合分析顯示,Prevena治療顯著降低了各種手術部位感染(SSI)、修正手術的風險以及縮短了住院時間。
*風險降低是基於從相關奇異比率和盛行率衍生的風險比率計算得出的。
†計算是基於本研究報告中相對患者群體發生率衍生的。統計顯著(p<0.05)。
詳情請參閱https://eifu.solventum.com的完整使用說明和限制。
積極風險管理 (PRM)
利用Prevena治療,接觸全面資源以將PRM納入您的實踐,藉由證明的術後好處,提升您的患者護理標準。
Prevena 治疗视频资源
NOTE:
Specific indications, limitations, contraindications, warnings, precautions and safety information exist for these products and therapies. Please consult a clinician and product instructions for use prior to application. This material is intended for healthcare professionals.
Indication(s) For Use / Intended Use:
The 3M™ Prevena™ Plus 125 Therapy Unit, when used with 3M™ Prevena™ Dressings (3M™ Prevena™ Plus Incision Management System), is intended to manage the environment of closed surgical incisions and surrounding intact skin in patients at risk for developing post-operative complications, such as infection, by maintaining a closed environment via the application of a negative pressure wound therapy system to the incision.
See full indications and limitations for use at hcbgregulatory.3m.com
參考資料:
- Antoniou G, Onwuka C, Antoniou S et al. Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of prophylactic negative pressure therapy for groin wounds in vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg 2019; 70 (5):1700-1710.
- Berríos-Torres, S. I., Umscheid, C. A., Bratzler, D. W., Leas, B., Stone, E. C., Kelz, R. R., Reinke, C. E., Morgan, S., Solomkin, J. S., Mazuski, J. E., Dellinger, E. P., Itani, K. M., Berbari, E. F., Segreti, J., Parvizi, J., Blanchard, J., Allen, G., Kluytmans, J. A., Donlan, R., & Schecter, W. P. (2017). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, 2017. JAMA Surgery, 152(8), 784. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904
- Ban, K. A., Minei, J. P., Laronga, C., Harbrecht, B. G., Jensen, E. H., Fry, D. E., Itani, K. M. F., Dellinger, P. E., Ko, C. Y., & Duane, T. M. (2017). American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 update. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 224(1), 59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.10.029