3M Bair Hugger systemer for temperaturstyring
3M Bair Hugger systemer for temperatur-styring
Vitenskapen om oppvarming: Håndtering av normotermi fra start til slutt
Forskjellen mellom et vellykket resultat for pasient og en komplisert restitusjon kan ofte bestemmes av noen få graders forskjell i kroppstemperatur. Utilsiktet perioperativ hypotermi er en vanlig, men unngåelig komplikasjon ved anestesi, kjent for å øke risikoen for kirurgiske sårinfeksjoner (SSI),6,7 forlenget restitusjonstid, og kan til og med øke dødelighetsraten.9 Men ved å følge en normotermiprotokoll som inkluderer kontinuerlig temperaturmonitorering og proaktive oppvarmingstiltak før anestesiinduksjon og gjennom operasjonen til restitusjon, kan hypotermi forhindres.
Start og avslutt pasientenes perioperative forløp med vårt 3M Bair Hugger system for temperaturstyring
Ved å opprettholde en normoterm kjernetemperatur kan en pasients opphold reduseres med 2,6 dager.11
Hvordan proaktivt håndtere normotermi gjennom det perioperative forløpet:
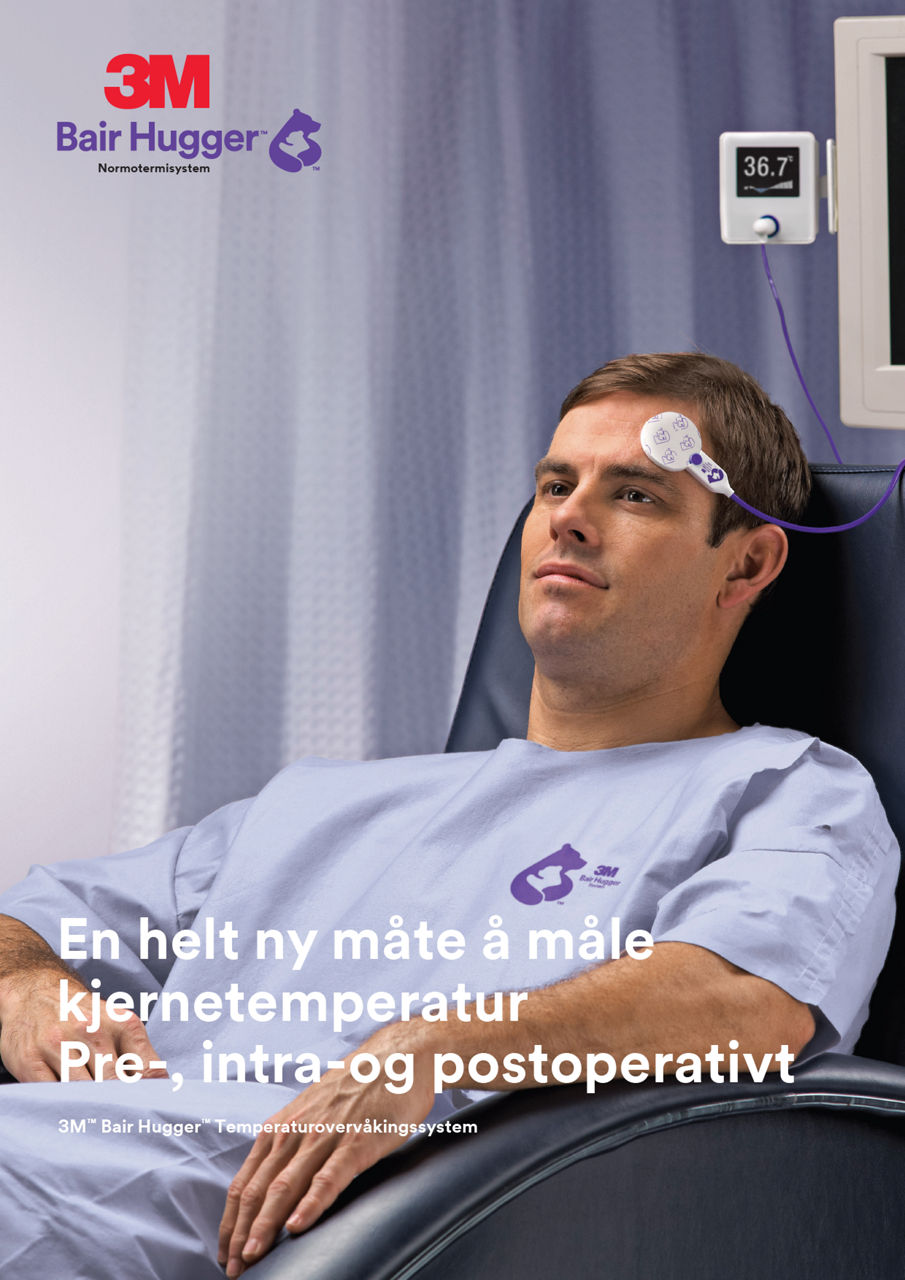
Mål aktivt pasientenes temperatur. Forvarm dem med 3Mᵀᴹ Bair Huggerᵀᴹ varmesystem for å bidra til å forhindre hypotermi.
Preoperativt (pre-op)
Forvarming før induksjon av anestesi bidrar til å opprettholde normotermi og redusere effekten av varmeredistribusjon forårsaket av anestesi.
Overvåk pasientenes kjernetemperatur under operasjonen med 3Mᵀᴹ Bair Huggerᵀᴹ temperaturmonitoreringssystem. Hjelp proaktivt med å oppnå og opprettholde normotermi med 3Mᵀᴹ Bair Huggerᵀᴹ varmesystem.
Intraoperativt (intra-op)
Fortsett å overvåke pasientenes temperatur. Varm dem med vårt 3Mᵀᴹ Bair Huggerᵀᴹ varmesystem for å beskytte pasienter mot utilsiktet perioperativ hypotermi.
Postoperativt (post-op)
Ved å opprettholde en pasients kjerne kroppstemperatur nær 36,5°C (36,6 + eller - 0,5°C), har det blitt vist at oppholdets lengde for pasienten reduseres med 2,6 dager.21
3M Bair Hugger systemer for temperaturstyring
MERK: Spesifikke indikasjoner, begrensninger, kontraindikasjoner, advarsler, forholdsregler og sikkerhetsinformasjon finnes for disse produktene og terapiene. Vennligst konsulter en kliniker og produktinstruksjoner for bruk før anvendelse. Kun etter forordning.
Ressurser for å opprettholde normotermi
Prosessen ved å overvåke temperatur kan være overveldende. Vi tilbyr nyttige ressurser for å hjelpe deg med å lære mer om våre løsninger og hvordan de kan hjelpe deg med å overvåke og opprettholde pasientenes normale kjernetemperatur — normotermi — gjennom hele deres perioperative forløp.
Fakta om oppvarming med varmluft
References:
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Lenhardt R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. Study of Wound Infection and Temperature Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(19):1209-1215.
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Lenhardt R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. Study of Wound Infection and Temperature Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(19):1209-1215.
- Bush HL Jr, Hydo LJ, et al. Hypothermia during elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: the high price of avoidable morbidity. J Vasc Surg. 1995;21:392-400; discussion 400-392.
- Lau A, Lowlaavar N, Cooke EM, et al. Effect of preoperative warming on intraoperative hypothermia: a randomized-controlled trial. Can J Anesth. 2018. doi.org/10.1007/s12630-018-1161-8.
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Lenhardt R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. NEJM. 1996 May 9; 334 (19): 1209-16.
- Horn, EP, Bein B, Bohm R, Steinfath M, Sahilin, and Hocker J. The effect of short time periods of pre-operative warming in the prevention of peri-operative hypothermia. Anaesthesia. 2012; 67: 612–617.
- Nelson G, Altman AD, Nick A, et al. Guidelines for pre- and intra-operative care in gynecologic/oncology surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society recommendations — Part I. Gynecologic Oncology. 2015; 2016; 140: 313-322.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Hypothermia: prevention and management in adults having surgery. Clinical Guideline [CG65]. (2016). https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg65/chapter/Recommendations#perioperative-care. Published April 2008. Updated December 2016. Accessed July 18, 2019.
- Forstot RM. The etiology and management of inadvertent perioperative hypothermia. J Clin Anesth. 1995;7:657-674.
- Leslie K, Sessler DI. Perioperative hypothermia in the high-risk surgical patient. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2003;17:485-498.
- Mahoney CB, Odom J. Maintaining intra-operative normothermia: a meta-analysis of outcomes with costs. AANA J. 1999;67(2):155-163.
- Schroeck H, Lyden AK, Benedict WL, Ramachandran SK. Time Trends and Predictors of Abnormal Postoperative Body Temperature in Infants Transported to the Intensive Care Unit. Anesthesiology Research and practice. 2016:7318137.
- Hooper VD, Chard R, Clifford T, Fetzer S, Fossum S, Godden B, Martinez EA, Noble KA, O’Brien D, Odom-Forren J, Peterson C, Ross J, Wilson L. ASPAN’s Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline for the Promotion of Perioperative Normothermia: Second Edition. J PeriAnesth Nurs. Vol 25, No 6 (December), 2010: pp 346-365.
- 3M Data on File: EM-05-297733, EM-05-711315.
- 3M™ Bair Hugger™ System Research Compendium, 2017 at: FAWFACTS.com.
- 3M Data on File: EM-05-233213, EM-05-268428.
- U.S. News and World Report. America’s Best Hospitals: the 2023-2023 Honor Roll and Overview. U.S. News and World Report website. Accessed December 2023 .https://health. usnews.com/health-care/best-hospitals/articles/best-hospitals-honor-roll-and-overview.
- Horn, EP, Bein B, Bohm R, Steinfath M, Sahilin, and Hocker J. The effect of short time periods of pre-operative warming in the prevention of peri-operative hypothermia. Anaesthesia. 2012; 67: 612–617.
- Lau A, Lowlaavar N, Cooke EM, et al. Effect of preoperative warming on intraoperative hypothermia: a randomized-controlled trial. Can J Anesth. 2018. doi.org/10.1007/s12630-018-1161-8.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Hypothermia: prevention and management in adults having surgery. Clinical Guideline [CG65]. (2016). https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg65/chapter/Recommendations#perioperative-care. Published April 2008. Updated December 2016. Accessed July 18, 2019.
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Lenhardt R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. NEJM. 1996 May 9; 334 (19): 1209-16.
- Horowitz PE, Delagarza MA, Pulaski JJ, Smith RA. Flow rates and warming efficacy with Hotline and Ranger blood/fluid warmers. Anesth Analg. 2004; 99 (3): 788-792.
- Nelson G, Altman AD, Nick A, et al. Guidelines for pre- and intra-operative care in gynecologic/oncology surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society recommendations — Part I. Gynecologic Oncology. 2015; 2016; 140: 313-322.
- Frank SM, Fleisher LA, Breslow MJ, et al. Perioperative maintenance of normothermia reduces the incidence of morbid cardiac events. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 1997; 277 (14): 1127-1134.
- Scott AV, Stonemetz JL, Wasey JO, Johnson DJ, Rivers RJ, Koch CG, et al. (2015) Compliance with Surgical Care Improvement Project for Body Temperature Management (SCIP Inf-10) Is Associated with Improved Clinical Outcomes. Anesthesiology. 123: 116–125.
- Anderson DJ. Strategies to prevent surgical site infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 2014; 35 (6): 605–627. doi: 10.1086/676022. Accessed December 15, 2016.
- Melling AC, Ali B, Scott EM, Leaper DJ. Effects of preoperative warming on the incidence of wound infection after a clean surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2001; 358 (9285): 876-880.
- Van Duren A. Patient Warming Plays a Significant Role in Satisfaction, Clinical Outcomes. Infection Control Today. 2008; 12 (6): 1-4 (reprint page numbers).
- Rajagopalan S, et al. The Effects of Mild Perioperative Hypothermia on Blood Loss and Transfusion Requirement. Anesthesiology. 2008; 108: 71-7.